Introduction
In the fast-paced landscape of data management, Data Vault 2.0 has emerged as a comprehensive framework, offering agility, scalability, and adaptability. At the heart of this framework lies the Business Vault, a critical component for effective data organization and analysis in modern enterprises.
In this article, we will check the key principles and strategies for designing a robust Business Vault within the context of Data Vault 2.0.
We also have a webinar on exactly this specific subject. Don’t miss it and watch the recording for free!
Understanding Data Vault 2.0
Data Vault 2.0 represents a paradigm shift in data architecture, distinguishing itself from traditional warehousing methods. Its flexibility and scalability make it ideal for organizations navigating the complexities of modern data ecosystems.
Data Vault 2.0 architecture follows a multi-layer approach, consisting of the Staging Layer, the Enterprise Data Warehouse Layer, and the Information Marts Layer. By dividing our data architecture into multiple layers, we can respond to both the needs of the technical teams (i.e., historization, auditability, and data integration), and the requirements of the business users (i.e., quick access to relevant, well-organized information). This integrated approach ensures a harmonious synergy between technical and business objectives.
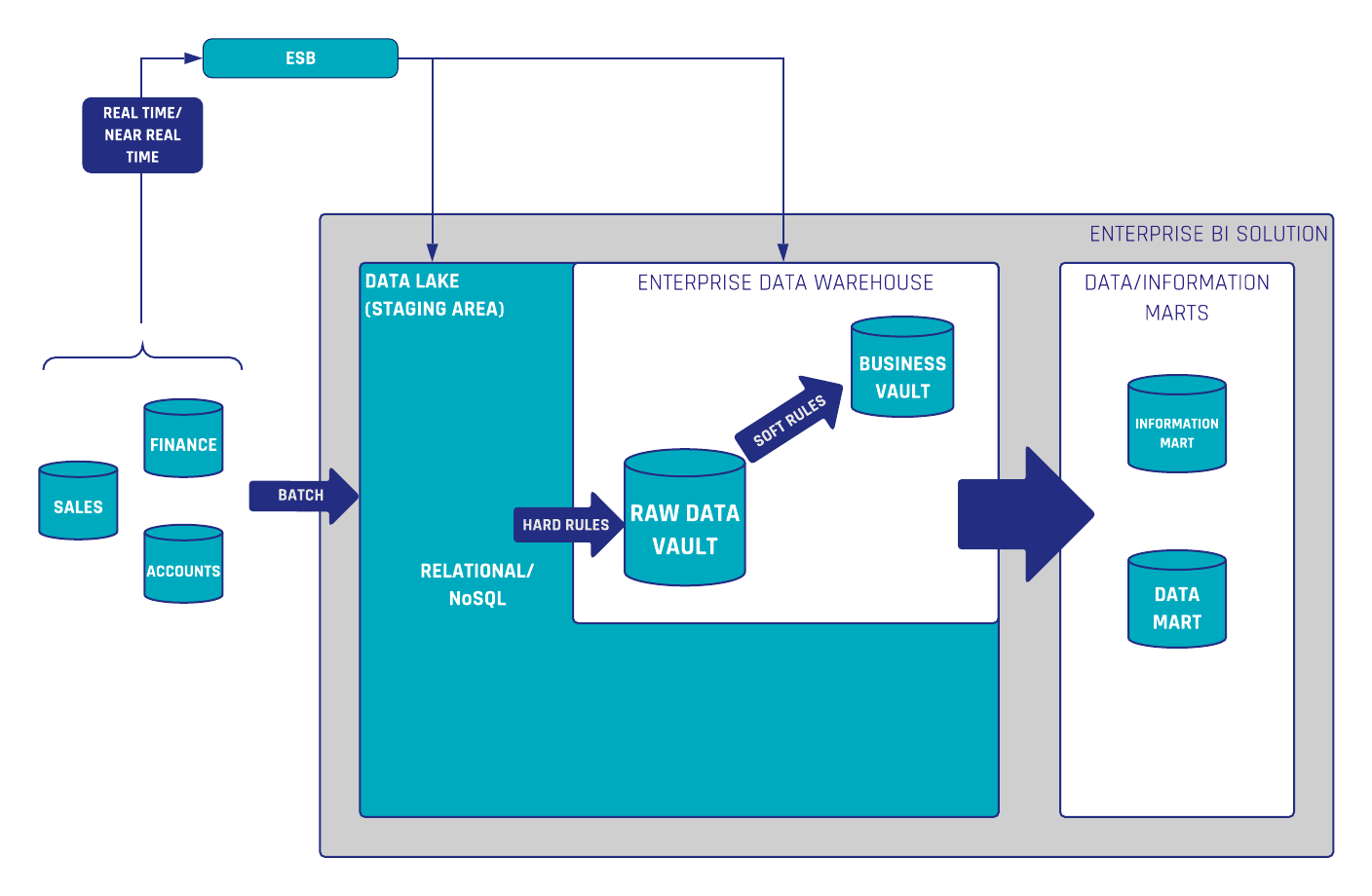
To achieve all these goals, Data Vault 2.0 proposes a subdivision inside the Enterprise Data Warehouse Layer: the Raw Vault and the Business Vault. The Raw Vault will receive and integrate the unaltered data from the source, while the Business Vault will translate the raw data into meaningful insights for informed decision-making.
Importance of Business Vault
The Business Vault serves as a middle ground between the Raw Vault and the Information Mart layers. It is an optional vault, sparsely generated on top of the Raw Vault and normally it is virtualized. Differently from the Raw Vault, in the Business Vault we will be applying soft business rules, i.e., those rules that change the data.
This layer will be created to serve the business in different ways, such as the generation of query assistance entities or by precomputing calculated fields that later will be used on downstream layers. In other words, the Business Vault will host business-rule changed data and its purpose is to ease the creation of the end-user structures.
Key Concepts of a Business Vault
A Business Vault will be modeled following the Data Vault 2.0 design principles. Nevertheless, it won’t necessarily follow the strict auditability requirements as the Raw Vault, as we can drop and recreate the Business Vault entities at any time. With the purpose of serving to populate the Information Mart more easily and efficiently, the entities will be created only if they are necessary for the business. This is also why the Business Vault usually keeps reusable business logic.
The types of entities we can typically find inside a Business Vault could be Point-In-Time (PIT) and Bridge Tables, for query assistance; Computed Satellites or Links, for storing computed data; and Exploration Links, for connecting Hubs that were not previously connected on the Raw Vault. Besides, any other entities that are created on top of the Raw Vault, using business logic and queried by the Information Marts layer, would belong to the Business Vault. For instance, we might need business logic to map instances of the same thing, thus creating a Business Same-as Link.
Final Remarks
In data management, Data Vault 2.0 encompassess different aspects such as data modeling, methodology, and architecture. Distinguished by its versatility, this framework places a significant emphasis on agility and adaptability. In this sense, at the core of Data Vault 2.0 architecture lies a pivotal concept, the Business Vault, a key player for efficient data organization and analysis in modern enterprises.
The Business Vault, a flexible optional layer, interprets raw data into actionable insights, applying soft business rules. Its purpose is to streamline end-user structure creation by hosting processed data. Entities are created selectively, keeping reusable business logic. In essence, the Business Vault ensures the efficient population of Information Marts by focusing on business-critical data.
Interested for more? Watch the webinar recording here for free!
– Hernan Revale (Scalefree)
Get Updates and Support
Please send inquiries and feature requests to [email protected].
For Data Vault training and on-site training inquiries, please contact [email protected] or register at www.scalefree.com.
To support the creation of Visual Data Vault drawings in Microsoft Visio, a stencil is implemented that can be used to draw Data Vault models. The stencil is available at www.visualdatavault.com.